How to Implement URL Redirects
Learn how to implement URL redirects using .htaccess, PHP header() function, and JavaScript. Discover 301 permanent, 302 temporary, and masked redirect methods ...

Learn how to implement link redirects using server-side methods (PHP, ASP), HTML meta refresh, and JavaScript. Understand SEO implications and best practices for 2025.
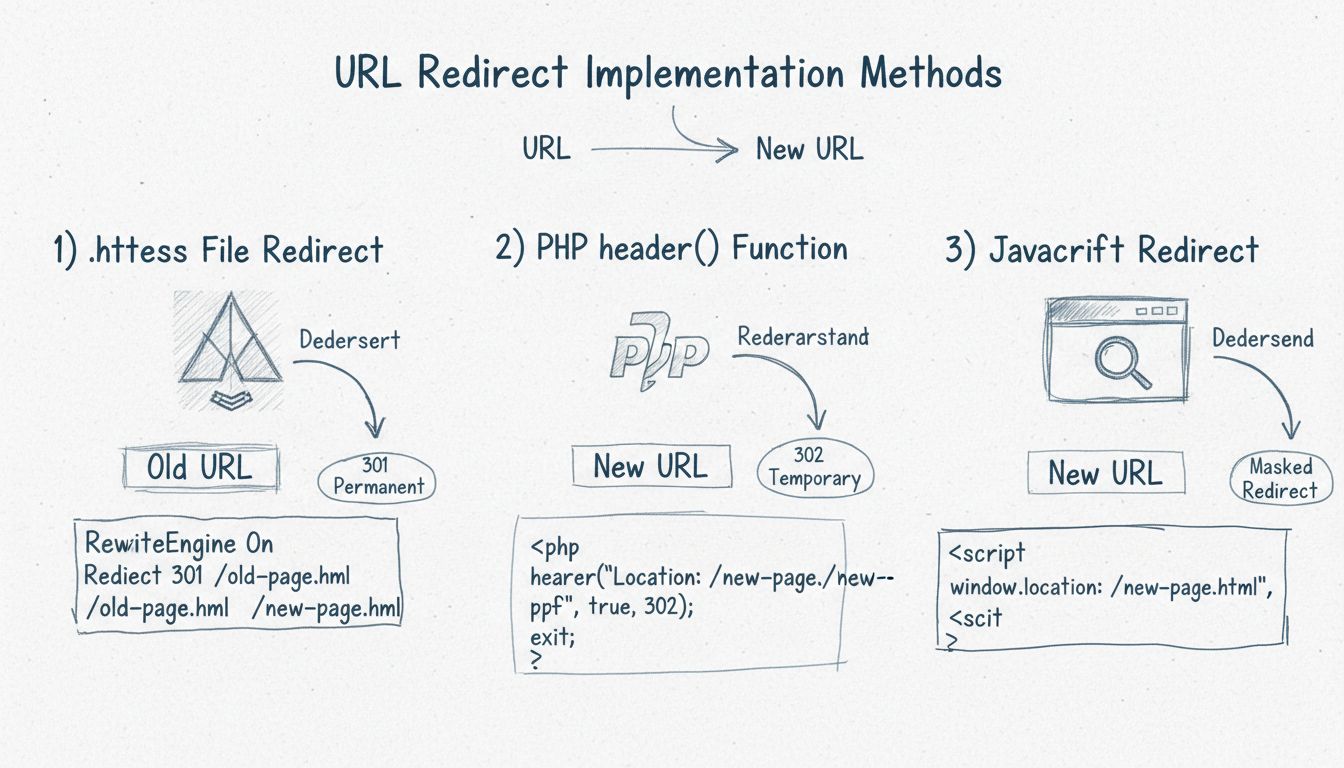
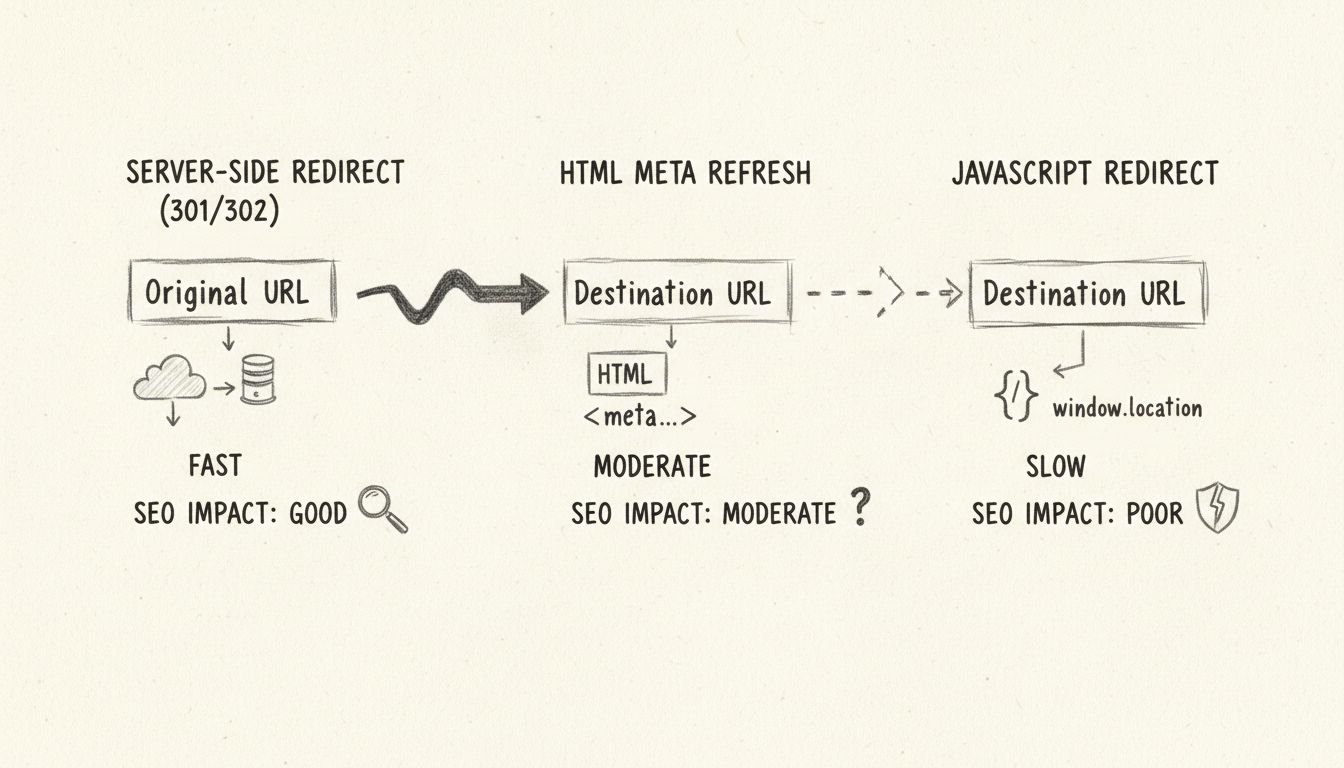
There are three main methods to create link redirects: server-side redirects (PHP, ASP, ColdFusion) which are SEO-friendly and fast, HTML meta refresh tags which are slower but simpler, and JavaScript redirects which work client-side but have SEO limitations. Server-side redirects using HTTP status codes (301 for permanent, 302 for temporary) are the recommended approach for most use cases.
Link redirects are a fundamental component of web management that automatically direct users from one URL to another. Whether you’re restructuring your website, managing affiliate links, or consolidating duplicate content, understanding the different redirect methods is essential for maintaining both user experience and search engine optimization. Each redirect method has distinct advantages and disadvantages that affect how quickly users are redirected, how search engines process the change, and the overall performance of your website.
The choice of redirect method depends on your specific needs, technical capabilities, and SEO requirements. Server-side redirects are universally preferred by search engines because they provide immediate, definitive signals about URL changes. However, situations may arise where client-side solutions like HTML meta refresh or JavaScript redirects become necessary due to platform limitations or specific use cases. Understanding when and how to use each method will help you implement redirects effectively and maintain your website’s search visibility.
Server-side redirects are the most reliable and SEO-friendly method for redirecting links. These redirects are processed by your web server before any content is sent to the user’s browser, making them the fastest and most efficient solution. When a user requests a URL that has a server-side redirect, the server immediately responds with an HTTP status code (such as 301 or 302) and the new location, allowing the browser to fetch the correct page without any delay.
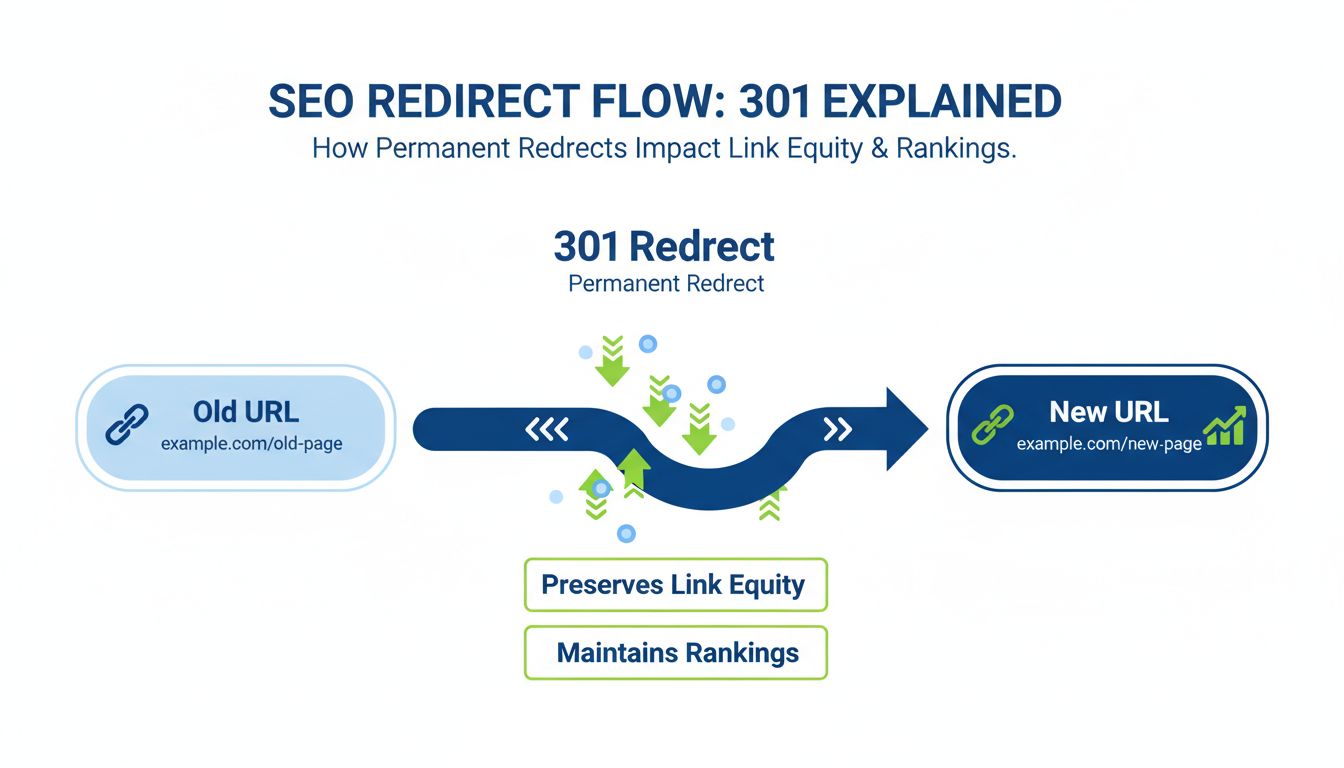
The primary advantage of server-side redirects is that search engines like Google and Bing can detect them instantly by reading the HTTP response headers. This means search engines don’t need to render JavaScript or parse HTML to understand that a page has moved. Server-side redirects also preserve link equity and ranking signals, which is crucial for maintaining your website’s search engine rankings when you restructure your site or move content to new URLs.
PHP is one of the most common server-side languages for implementing redirects. The header() function in PHP allows you to send HTTP headers to the browser, including redirect instructions. To implement a basic PHP redirect, you place the redirect code at the very beginning of your PHP file, before any HTML output. The critical rule is that the header() function must be called before any content is sent to the browser, including whitespace or HTML tags.
Here’s the basic syntax for a PHP redirect:
<?php
header("Location: https://www.example.com/new-page");
exit;
?>
The exit; statement is essential because it stops the script from executing any further code after the redirect is initiated. For SEO purposes, you can specify HTTP status codes to indicate whether the redirect is permanent or temporary. A 301 status code indicates a permanent redirect, which tells search engines to update their index and transfer all ranking signals to the new URL. A 302 status code indicates a temporary redirect, which tells search engines to keep the original URL in their index because it may return in the future.
<?php
// Permanent redirect (301)
header("Location: https://www.example.com/new-page", true, 301);
exit;
?>
ASP (Active Server Pages) and ColdFusion are alternative server-side technologies that also support redirects. In ASP, you use the Response.Redirect() method to send users to a new URL. ColdFusion uses the <cflocation> tag to accomplish the same result. Both methods work similarly to PHP redirects by sending HTTP headers to the browser before any page content is rendered.
HTML meta refresh is a client-side redirect method that uses a special meta tag placed in the <head> section of your HTML document. This method instructs the browser to refresh the page and load a new URL after a specified number of seconds. The syntax for an HTML meta refresh redirect is straightforward:
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0; url=https://www.example.com/new-page">
The content attribute contains two values: the number of seconds to wait before redirecting (0 for immediate), and the URL to redirect to. While HTML meta refresh is simple to implement and doesn’t require server configuration, it has significant drawbacks for SEO and user experience. Search engines are slower to recognize meta refresh redirects compared to server-side redirects because they must parse the HTML to find the redirect instruction. Additionally, there’s no guarantee that search engines will pass full link equity to the destination URL, potentially resulting in a loss of ranking signals.
From a user experience perspective, HTML meta refresh redirects are also slower than server-side redirects because the browser must first load the original page, parse the HTML, and then initiate the redirect. This creates a noticeable delay for users, especially on slower connections. For these reasons, HTML meta refresh should only be used when server-side redirects are not available.
JavaScript redirects are implemented entirely on the client side, meaning the redirect logic is executed in the user’s browser after the page has loaded. The most common JavaScript redirect method uses the window.location.href property or the window.location.replace() method. These approaches are useful for conditional redirects, such as redirecting users based on their device type, login status, or other dynamic conditions.
<script>
window.location.href = "https://www.example.com/new-page";
</script>
The window.location.replace() method is generally preferred over window.location.href because it replaces the current page in the browser history, preventing users from using the back button to return to the original URL. This is particularly useful when you want to prevent users from accessing outdated or deprecated pages.
<script>
window.location.replace("https://www.example.com/new-page");
</script>
However, JavaScript redirects have significant limitations for SEO. Google must render the page to detect JavaScript redirects, which adds extra processing time and may not always happen due to crawl budget constraints. Other search engines like Bing and smaller search engines may not execute JavaScript at all, meaning they won’t detect your redirects. Additionally, JavaScript redirects waste crawl budget because search engines must crawl and render the page to find the redirect, consuming more resources than a simple HTTP header check.
| Method | Implementation | Speed | SEO Impact | Browser Support | Search Engine Support | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Server-Side (301/302) | PHP, ASP, ColdFusion | Fastest | Excellent | 100% | 100% | Permanent or temporary URL changes |
| HTML Meta Refresh | HTML meta tag | Moderate | Good | 100% | 95% | Simple redirects when server access unavailable |
| JavaScript | window.location | Slow | Poor | 70% | 70% | Conditional redirects, device detection |
Conditional redirects allow you to redirect users based on specific criteria, such as their device type, login status, geographic location, or referrer source. These advanced redirects are typically implemented using server-side languages like PHP or JavaScript, depending on whether you need the redirect to happen on the server or in the browser. A conditional redirect checks a specific condition and only executes the redirect if that condition is met, providing flexibility for complex website scenarios.
A common use case for conditional redirects is redirecting users to a mobile-optimized version of your website based on their device. Using PHP, you can check the user agent string to detect mobile devices and redirect accordingly. Another practical application is redirecting users after they successfully log in to a members-only area of your website. You can check the session variable to determine if a user is authenticated, and if not, redirect them to the login page. For A/B testing scenarios, you can randomly redirect users to different versions of a page to measure which performs better.
For affiliate marketers using PostAffiliatePro, conditional redirects are particularly valuable for managing complex affiliate link structures. You can redirect users based on their referrer source, create A/B testing scenarios, or implement device-specific landing pages. PostAffiliatePro’s advanced link management system integrates seamlessly with your redirect strategy, allowing you to track clicks, monitor conversions, and optimize your affiliate campaigns with precision. The platform’s built-in analytics help you understand which redirects are performing best and where your traffic is coming from.
When implementing redirects, it’s crucial to follow SEO best practices to ensure that search engines properly understand your URL changes and maintain your website’s ranking signals. First, always use permanent redirects (301 status codes) when a page’s URL has changed permanently. This tells search engines to update their index and transfer all ranking signals to the new URL. Reserve temporary redirects (302 status codes) for situations where you plan to restore the original URL in the future, such as during website maintenance or seasonal campaigns.
Second, ensure consistency in your redirect signals by updating related elements on your website. Update the canonical link tag on alternate pages to point to the redirect target, modify internal links to point directly to the new URL instead of the old one, and add the new URL to your XML sitemap while removing the old URL. Additionally, always redirect to the HTTPS version of a page rather than the HTTP version, as HTTPS is a ranking signal that Google considers when determining canonical URLs. This consistency helps search engines understand your site structure and prevents confusion about which URL should be indexed.
Third, avoid redirect chains where one URL redirects to another URL, which then redirects to a third URL. Redirect chains waste crawl budget and slow down page loading for users. Instead, redirect directly from the old URL to the final destination. Monitor your website regularly using tools like Google Search Console or specialized redirect checkers to identify and fix any redirect issues before they impact your SEO performance. Implementing a redirect audit schedule ensures that your website maintains optimal performance and search visibility over time.
To maintain optimal website performance and SEO health, you should regularly audit your website to identify all redirects and ensure they’re implemented correctly. For server-side redirects, you can use website crawlers with proper HTTP header analysis to detect redirect chains and status codes. For JavaScript redirects, you need a crawler that can render JavaScript, as these redirects won’t be visible in HTTP headers alone. Professional SEO tools can analyze your entire site structure and provide detailed reports on all redirects.
Chrome extensions like “Redirect Path” provide a quick way to check redirect details while browsing your website. When you click on the extension icon, it displays the redirect type, status code, and destination URL. This is useful for spot-checking redirects during website audits, though it’s not practical for auditing an entire website. For comprehensive redirect audits, use professional SEO crawlers that can analyze your entire site structure and identify all redirects, redirect chains, and potential issues. These tools help you maintain a healthy redirect structure that supports both user experience and SEO performance.
PostAffiliatePro’s link management system provides built-in redirect tracking and monitoring capabilities, allowing you to manage all your affiliate redirects from a centralized dashboard. You can track click-through rates, monitor redirect performance, and identify any issues that might be affecting your affiliate marketing campaigns. This integrated approach ensures that your redirects are working correctly and contributing to your overall affiliate marketing success. The platform’s comprehensive reporting features give you visibility into every aspect of your redirect performance.
One of the most common issues when implementing PHP redirects is the “headers already sent” error. This error occurs when something is sent to the browser before the header() function is called, such as HTML content, whitespace, or PHP output. To fix this error, ensure that your redirect code is placed at the very beginning of your PHP file, before any HTML or output statements. Check for whitespace before the opening <?php tag, as even a single space can cause this error. Additionally, verify that no files included before the redirect contain any output.
Another common issue is redirect loops, where URL A redirects to URL B, and URL B redirects back to URL A. This creates an infinite loop that prevents users from accessing either page and wastes server resources. To prevent redirect loops, carefully plan your redirect structure and test all redirects thoroughly before deploying them to your live website. Use redirect checking tools to identify and fix any loops before they impact your users. Document your redirect structure to ensure that future changes don’t accidentally create loops.
If your redirects aren’t working as expected, clear your browser cache to ensure you’re seeing the current version of your website. Browser caching can cause old redirects to persist even after you’ve updated your redirect rules. If the issue persists after clearing your cache, try accessing your website from a different browser or device to rule out browser-specific issues. Finally, check your server logs to see if there are any error messages that might indicate what’s causing the redirect to fail. Server logs often contain valuable information about redirect failures and other issues affecting your website.
PostAffiliatePro provides advanced link management, tracking, and redirect capabilities built specifically for affiliate marketing. Manage all your redirects, track clicks, and optimize conversions in one powerful platform.

Learn how to implement URL redirects using .htaccess, PHP header() function, and JavaScript. Discover 301 permanent, 302 temporary, and masked redirect methods ...
Learn why redirects are crucial for SEO and user experience. Discover how 301 redirects preserve link equity, prevent 404 errors, and maintain search rankings. ...
A redirect link is a line of text that sends the visitor to another website upon clicking on it. Find out more in the article.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.