
What is a Good Cost Per Lead? 2025 CPL Benchmarks & Optimization Guide
Discover what constitutes a good cost per lead in 2025. Learn industry benchmarks, CPL formulas, and proven strategies to optimize your lead generation costs wi...

Discover the true cost per lead across industries in 2025. Learn what factors influence lead pricing, industry benchmarks, and how PostAffiliatePro helps optimize your lead generation ROI.
The cost per lead varies significantly from $10 to $500+ depending on industry, lead quality, and source. High-value sectors like legal services ($320) and healthcare ($285) command premium prices, while retail and e-commerce typically cost $20-$75 per lead. PostAffiliatePro helps optimize lead costs through intelligent affiliate tracking and performance-based pricing models.
The cost per lead (CPL) has become one of the most critical metrics for businesses evaluating their marketing efficiency and return on investment. In 2025, the average cost per lead across all industries ranges from $10 to over $500, with significant variations based on multiple factors including industry vertical, lead quality, geographic location, and the marketing channels employed. Understanding these costs is essential for budgeting, forecasting, and optimizing your lead generation strategy to ensure maximum profitability and sustainable business growth.
The concept of cost per lead is straightforward but powerful: it represents the total amount a company spends on marketing and sales efforts divided by the number of leads generated during a specific period. This metric provides clear visibility into marketing efficiency and helps identify which channels and strategies deliver the best return on investment. By tracking CPL consistently, businesses can make data-driven decisions about resource allocation and identify opportunities to reduce costs while maintaining or improving lead quality.
Calculating your cost per lead is fundamental to understanding your marketing performance and making informed budget decisions. The formula is simple but requires accurate data collection across all marketing channels and activities. Here’s how to calculate it properly:
CPL = Total Marketing Spend ÷ Number of Leads Generated
To implement this formula effectively, you need to include all costs associated with lead generation. This encompasses paid advertising expenses on platforms like Google Ads, Facebook, and LinkedIn; content creation costs including blog posts, videos, and downloadable resources; marketing technology tools such as CRM systems, email marketing platforms, and analytics software; and sales team efforts including salaries, commissions, and training related to lead acquisition and nurturing activities.
For example, if your company invested $5,000 in marketing activities during a month and generated 250 leads from those efforts, your cost per lead would be $20 ($5,000 ÷ 250 = $20). However, this calculation becomes more sophisticated when you track CPL across different channels, as some channels may have significantly higher or lower costs than others. Advanced businesses segment their CPL calculations by channel, campaign, and even by lead quality tier to identify which specific efforts deliver the best results.
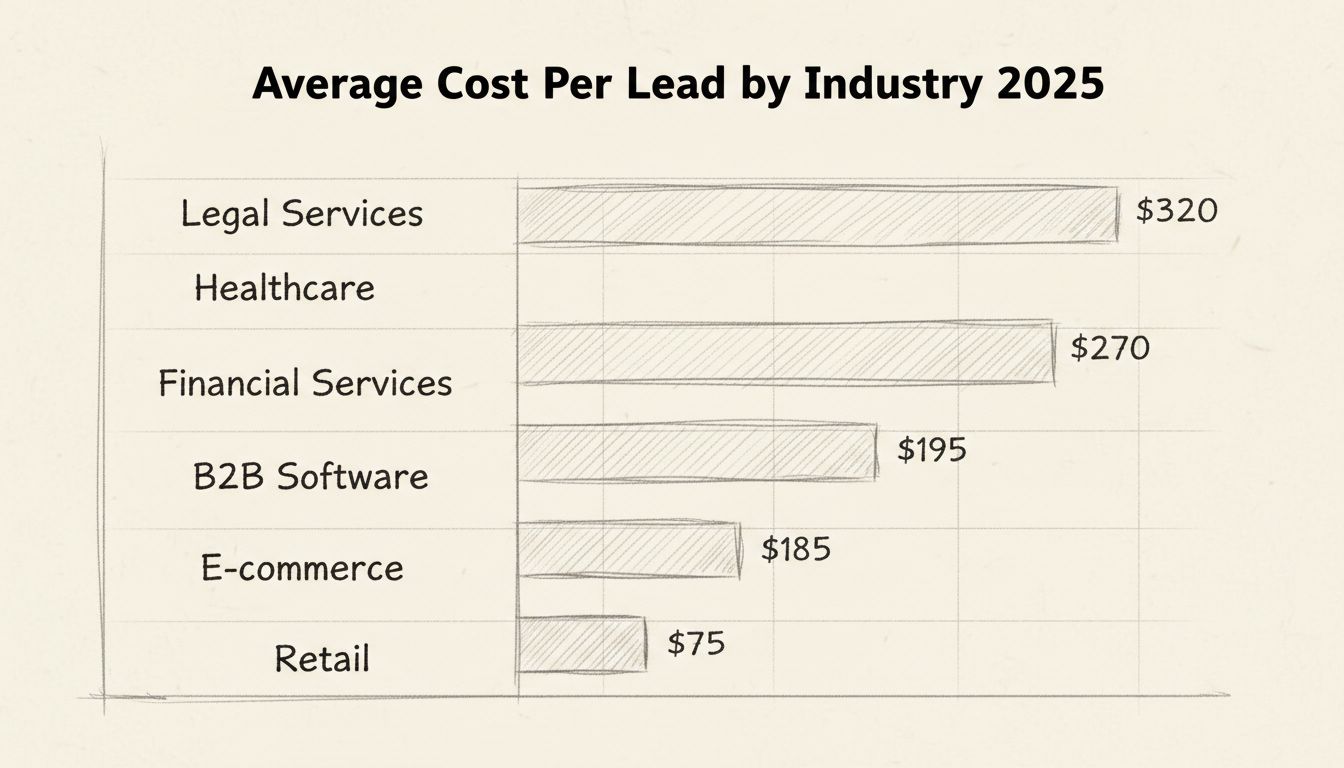
Lead costs vary dramatically across different industries, reflecting differences in competition levels, customer lifetime value, sales cycle complexity, and regulatory requirements. Understanding your industry’s benchmarks is crucial for setting realistic budgets and identifying whether your current CPL is competitive or requires optimization.
High-Cost Industries ($250+): Legal services consistently rank as the most expensive sector for lead generation, with an average CPL of $320. This premium pricing reflects the high value of legal clients, complex sales processes, and intense competition among law firms for qualified prospects. Financial services follows closely at $270 per lead, driven by strict regulatory requirements, the need for highly qualified leads, and the substantial revenue potential of each client relationship. Healthcare leads average $285, reflecting the complexity of healthcare purchasing decisions, compliance requirements, and the specialized knowledge required to effectively market healthcare solutions. These industries justify higher lead costs because a single client can generate tens of thousands of dollars in lifetime revenue.
Mid-Range Industries ($100-$250): Real estate leads average $220 per lead, with costs varying significantly based on geographic location and property type. B2B software companies typically pay $195 per lead due to longer sales cycles and the need for highly targeted, decision-maker level contacts. Manufacturing leads cost approximately $165, reflecting the complexity of industrial purchasing processes and the need for technical expertise in lead qualification. Technology sector leads average $155, driven by competitive markets and the need for specialized technical knowledge among prospects.
Lower-Cost Industries ($20-$100): E-commerce businesses typically pay $85 per lead, benefiting from high transaction volumes and lower customer acquisition costs. Retail leads average $75, supported by impulse buying behavior and broad market appeal. Education sector leads cost approximately $100, while travel and tourism leads average $55 per lead due to seasonal demand patterns and high transaction volumes.
| Industry | Average CPL | Range | Lead Quality Score | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Services | $320 | $250-$400 | 4.2/5 | High client value, complex sales, intense competition |
| Healthcare | $285 | $200-$350 | 4.5/5 | Regulatory compliance, specialized knowledge required |
| Financial Services | $270 | $200-$350 | 4.3/5 | Strict regulations, high lifetime value |
| Real Estate | $220 | $150-$300 | 3.8/5 | Location-dependent, seasonal variations |
| B2B Software | $195 | $150-$250 | 4.1/5 | Long sales cycles, decision-maker targeting |
| Manufacturing | $165 | $120-$210 | 4.0/5 | Complex purchasing, technical requirements |
| Technology | $155 | $100-$200 | 3.7/5 | Competitive market, rapid changes |
| Insurance | $145 | $100-$180 | 3.9/5 | High lifetime value, compliance needs |
| E-commerce | $85 | $50-$120 | 3.2/5 | High volume, lower margins |
| Retail | $75 | $40-$100 | 3.0/5 | Price-sensitive customers, impulse buying |
Multiple interconnected factors determine how much you’ll pay for leads in your specific market and industry. Understanding these factors allows you to anticipate cost changes, negotiate better rates with lead providers, and identify opportunities to optimize your spending.
Industry Competition and Demand: The level of competition within your industry directly impacts lead costs. Highly competitive sectors like financial services and technology experience bidding wars for advertising space, driving up costs across all channels. When many companies compete for the same audience, advertising platforms increase prices, and lead generation providers charge premium rates. Conversely, emerging industries or niche markets often offer lower lead costs because fewer competitors are actively bidding for attention. Monitoring competitive activity in your space helps you understand whether rising CPL reflects market trends or indicates inefficiencies in your campaigns.
Lead Quality and Intent Signals: Higher-quality leads that demonstrate clear buying intent command significantly higher prices than generic leads. A lead that has visited your pricing page multiple times, downloaded a product comparison guide, and engaged with your sales team shows stronger purchase intent than someone who simply filled out a generic form. Intent-based targeting, which identifies prospects actively researching solutions like yours, typically costs 30-50% more than broad demographic targeting but delivers substantially higher conversion rates. The relationship between lead quality and cost is not linear—premium quality leads often deliver 3-5x better conversion rates, making their higher cost justified by superior ROI.
Geographic Location and Market Saturation: Geographic factors significantly influence lead costs. Leads from saturated markets like North America and Western Europe typically cost 40-60% more than leads from emerging markets. Within the United States, leads from major metropolitan areas command higher prices than rural areas due to greater competition and higher customer lifetime values. International expansion often reveals opportunities for lower-cost leads, though these may require additional nurturing and localization efforts.
Sales Cycle Length and Complexity: Industries with longer, more complex sales cycles typically have higher lead costs because more resources are required to nurture prospects through the buying journey. B2B software companies with 6-12 month sales cycles pay significantly more per lead than e-commerce businesses with 1-2 day purchase decisions. The extended engagement required in complex sales justifies higher upfront lead acquisition costs because the potential customer lifetime value is substantially higher.
Marketing Channel Selection: Different marketing channels deliver leads at vastly different costs. Paid search advertising (Google Ads) typically costs $50-$150 per lead but delivers high-intent prospects actively searching for solutions. Social media advertising ranges from $10-$40 per lead but often requires more nurturing. Content marketing and SEO deliver leads at $15-$50 per lead but require significant upfront investment and time to generate results. Email marketing remains one of the most cost-effective channels at $20-$30 per lead when you have an existing audience. Referral programs often deliver leads at $10-$30 per lead with superior conversion rates.
The distinction between paid and organic lead generation costs represents one of the most important strategic decisions in marketing. Paid channels deliver immediate results but require continuous investment, while organic channels build long-term assets that generate leads indefinitely. Most successful companies employ a blended approach that balances immediate needs with long-term sustainability.
Paid lead generation through advertising platforms, sponsored content, and paid partnerships delivers leads quickly but at higher per-unit costs. Google Ads averages $66-$70 per lead in 2025, with significant variation by industry and keyword competitiveness. LinkedIn advertising for B2B leads ranges from $50-$100 per lead depending on targeting specificity. Facebook and Instagram advertising delivers leads at $10-$40 per lead for consumer-focused businesses. The advantage of paid channels is predictability—you can forecast lead volume and costs with reasonable accuracy. The disadvantage is that lead generation stops immediately when you stop spending.
Organic lead generation through content marketing, SEO, and referral programs costs significantly less per lead but requires substantial upfront investment and patience. SEO-driven leads typically cost $15-$50 per lead once the content ranks, but initial content creation and optimization can require months of effort. Content marketing through blogs, whitepapers, and webinars generates leads at $20-$50 per lead but requires consistent content production. Referral programs deliver leads at $10-$30 per lead with exceptional conversion rates, but building a strong referral network takes time. The advantage of organic channels is sustainability—once established, they generate leads indefinitely with minimal ongoing investment. The disadvantage is the time required to see results.
Reducing your cost per lead without sacrificing quality requires a strategic, data-driven approach that focuses on efficiency rather than simply cutting budgets. The goal is to generate more qualified leads at lower cost, not to generate more leads regardless of quality.
Implement Precise Audience Targeting: Narrow your target audience to focus on prospects most likely to convert. Instead of targeting “all business owners,” target “SaaS business owners with 50-500 employees in the technology sector.” This specificity reduces wasted ad spend on unqualified prospects and lowers your overall CPL. Advanced targeting using behavioral data, intent signals, and demographic information can reduce CPL by 30-40% while improving conversion rates by 50-100%.
Leverage Multiple Channels Strategically: Different channels work better for different audiences and industries. A blended approach that combines high-intent paid channels with cost-effective organic channels typically delivers better results than relying on a single channel. For example, using paid search for immediate lead generation while simultaneously building organic content assets creates a sustainable, cost-efficient lead generation engine.
Optimize Landing Pages and Forms: Every element of your lead capture process impacts both quantity and quality. Simplified forms with fewer fields generate more leads but may capture less useful information. Testing different form lengths, field types, and page designs through A/B testing can reduce CPL by 20-30% while improving lead quality. Progressive profiling, which captures information gradually across multiple interactions, often delivers better results than comprehensive forms.
Implement Lead Scoring and Qualification: Not all leads have equal value. Implementing a lead scoring system that identifies high-potential prospects allows you to focus sales resources on the most promising opportunities. This improves conversion rates and reduces the effective cost per customer acquired, even if the cost per lead remains constant. Automated lead qualification through chatbots or AI-powered systems can pre-qualify leads before they reach your sales team, improving efficiency.
Use Marketing Automation and Nurturing: Automated email sequences and nurturing campaigns reduce the manual effort required to move leads through your sales funnel. By automating repetitive tasks, you reduce labor costs while improving consistency and response times. Marketing automation platforms can reduce the cost of lead nurturing by 40-50% while improving conversion rates.
Different pricing models for lead generation services offer various advantages and disadvantages depending on your business model and risk tolerance. Understanding these models helps you negotiate better terms with lead providers and structure your own affiliate programs effectively.
Cost Per Lead (CPL): The most common model charges a fixed price for each qualified lead delivered. This model is straightforward and aligns costs directly with lead volume. However, it can incentivize quantity over quality if not carefully managed. CPL pricing typically ranges from $10-$500+ depending on industry and lead quality. This model works well for businesses with predictable conversion rates and clear lead quality standards.
Cost Per Appointment (CPA): This model charges only when a lead books a meeting or appointment with your sales team. It’s particularly effective for B2B businesses where the primary goal is securing qualified meetings. CPA pricing typically ranges from $50-$3,000 depending on the seniority level of the contact and industry. This model reduces risk because you only pay for leads that demonstrate sufficient interest to book time with your team.
Performance-Based Pricing: This model ties costs to actual business results such as revenue generated or customers acquired. It’s ideal for high-value B2B transactions where lead quality directly impacts revenue. Performance-based pricing typically involves a percentage of revenue generated (1-3% of deal value) or a fixed fee per customer acquired. This model aligns incentives perfectly but requires robust tracking and attribution systems.
Flat Fee Retainer: A fixed monthly or periodic charge provides predictable costs and revenue. This model works well for ongoing lead generation relationships where volume is relatively stable. Retainer pricing typically ranges from $2,000-$50,000+ per month depending on expected lead volume and quality. This model provides budget certainty but may not align costs with actual results.
Hybrid Models: Combining multiple pricing approaches, such as a base CPL rate with performance bonuses for high-quality leads or conversion-based incentives, can align incentives while maintaining cost predictability. Hybrid models are increasingly popular because they balance risk between buyer and seller.
Regularly comparing your lead costs against industry benchmarks helps identify whether your current spending is competitive and whether optimization opportunities exist. However, benchmarks should be used as starting points rather than absolute targets, as your specific situation may justify different costs.
To benchmark effectively, calculate your CPL across all channels and compare against industry averages. If your CPL significantly exceeds industry averages, investigate whether this reflects higher lead quality, different targeting criteria, or inefficiencies in your campaigns. If your CPL is significantly below average, verify that you’re not sacrificing quality for cost. Track your CPL monthly and identify trends—rising CPL may indicate increasing competition or platform cost increases, while declining CPL may reflect improved campaign optimization.
Consider also tracking cost per qualified lead (CPQL), which measures the cost of leads that meet your specific quality criteria, and cost per customer acquired (CAC), which measures the total cost of acquiring a paying customer. These metrics provide more complete pictures of your lead generation efficiency than CPL alone. A low CPL combined with a high CAC suggests quality issues, while a high CPL combined with a low CAC suggests you’re investing appropriately in lead quality.
The cost per lead in 2025 varies dramatically based on industry, lead quality, geographic location, and marketing channels employed. While industry averages provide useful benchmarks, your specific costs should reflect your unique business model, target audience, and quality requirements. By understanding the factors that influence lead costs, implementing strategic optimization techniques, and regularly benchmarking against industry standards, you can build a cost-efficient lead generation engine that delivers sustainable business growth.
PostAffiliatePro empowers businesses to optimize their lead generation costs through intelligent affiliate tracking, performance-based commission structures, and comprehensive analytics. By leveraging PostAffiliatePro’s platform, you can ensure that every dollar spent on lead generation delivers measurable results, track lead quality throughout your sales funnel, and scale your affiliate program profitably. Whether you’re managing internal lead generation efforts or running an affiliate program, PostAffiliatePro provides the tools and insights needed to maximize ROI and minimize wasted spending.
Stop overpaying for leads. PostAffiliatePro's advanced affiliate tracking and performance-based commission system ensures you only pay for results. Track every lead, measure ROI accurately, and scale your affiliate program profitably.

Discover what constitutes a good cost per lead in 2025. Learn industry benchmarks, CPL formulas, and proven strategies to optimize your lead generation costs wi...

Learn how to calculate cost per lead (CPL) with our comprehensive guide. Discover the formula, industry benchmarks, and strategies to reduce your CPL and improv...
A cost per lead (CPL) model represents a payment model for internet promotion. Affiliates are paid for each lead generated by the merchant.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.