What is the Hardest Computer Virus to Remove? A Technical Guide
Discover why rootkits, bootkits, and fileless malware are the hardest viruses to remove. Learn detection methods, removal strategies, and prevention techniques ...

Learn how anti-malware protects your business from malicious software, phishing attacks, and network compromise. Discover detection methods, prevention strategies, and best practices for enterprise security.
Anti-malware protects your business by detecting and blocking malicious software through signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, and real-time scanning. It prevents phishing attacks, ransomware infections, and data theft while reducing the risk of network compromise and operational downtime.
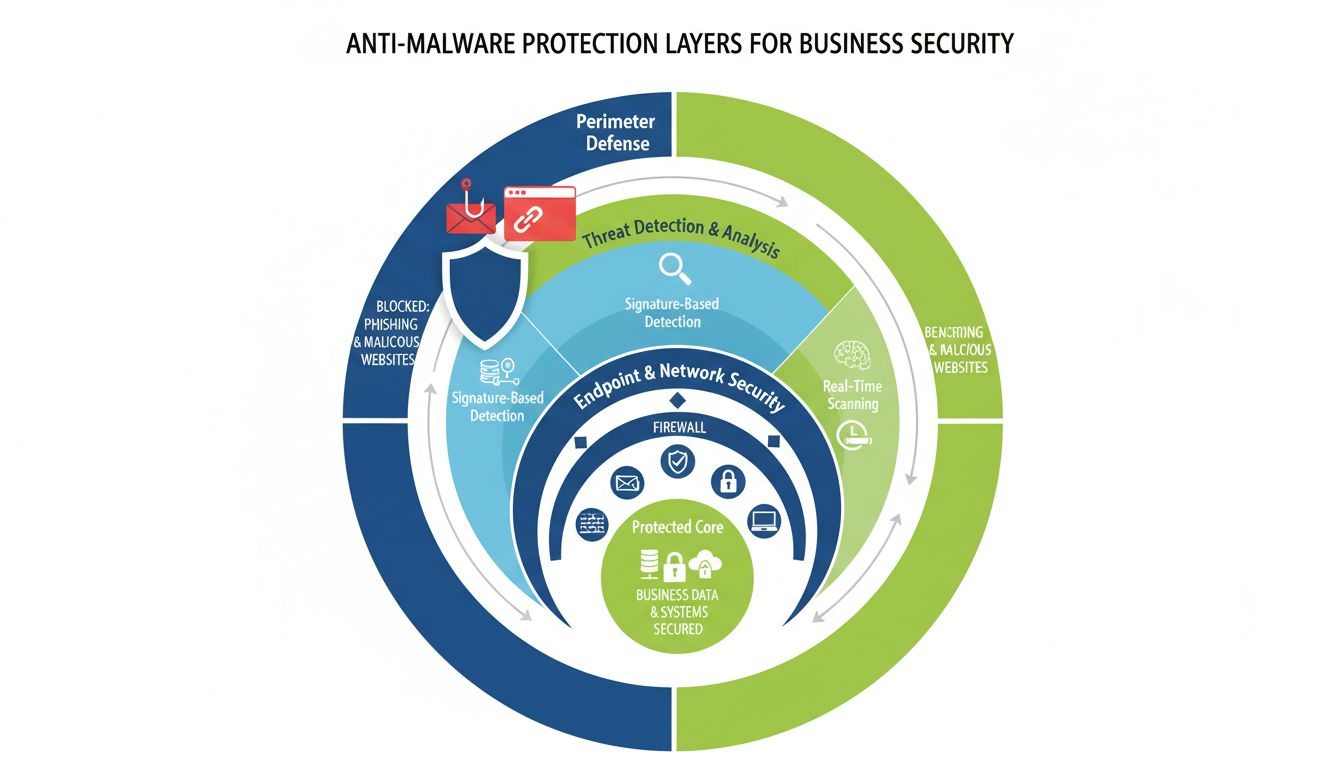
Anti-malware software serves as a critical defensive layer in modern business cybersecurity infrastructure. In 2025, with cyber attacks increasing by 21% compared to the previous year and organizations facing increasingly sophisticated threats, understanding how anti-malware protects your business has become essential for any organization handling sensitive data. Anti-malware is not a single tool but rather a comprehensive security solution that combines multiple detection and prevention technologies to identify, block, and remove malicious software before it can compromise your systems, steal data, or disrupt operations.
The importance of anti-malware protection extends beyond simple virus removal. Modern anti-malware solutions protect against a diverse range of threats including ransomware, spyware, trojans, worms, adware, rootkits, and fileless malware. Each of these threats operates differently and requires specific detection and removal strategies. By implementing robust anti-malware protection, businesses can significantly reduce their exposure to cyber threats, maintain business continuity, protect customer trust, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Modern anti-malware solutions employ multiple detection methodologies working in concert to identify threats at different stages of an attack. Signature-based detection represents the traditional approach, where anti-malware software maintains a comprehensive database of known malware signatures—unique strings of data or characteristics that identify previously cataloged threats. When files are scanned, the software compares them against this database, flagging any matches as potential malware. This method is highly effective for known threats but requires regular updates to remain current with emerging malware variants.
Behavioral analysis represents a more advanced detection approach that monitors system activity, file access patterns, and process behavior to identify suspicious actions that deviate from normal operations. Rather than relying solely on signature matching, behavioral analysis examines how programs interact with the operating system, what files they access, and what network connections they establish. This methodology proves particularly valuable for detecting zero-day exploits and previously unknown malware variants that lack established signatures. When a program exhibits characteristics common to malware—such as attempting to encrypt large numbers of files rapidly or accessing sensitive system areas without authorization—behavioral analysis flags it for further investigation or automatic removal.
Heuristic analysis combines elements of both approaches by examining code characteristics and behaviors that typically indicate malicious intent. This technique can identify modified versions of known malware and detect new threats that share behavioral patterns with established malware families. Machine learning and artificial intelligence have enhanced heuristic capabilities significantly, allowing modern anti-malware solutions to analyze vast datasets of threat intelligence and identify complex patterns that might indicate novel attacks.
Sandboxing provides another critical detection mechanism by executing suspicious files in an isolated, virtual environment separate from the actual operating system. This contained environment allows security analysts to observe malware behavior without risking the integrity of production systems. The malware typically believes it has full system access while actually operating within restricted boundaries, revealing its true intentions before it can cause damage. Some advanced malware recognizes sandboxed environments and suppresses malicious behavior, which is why modern solutions combine sandboxing with other detection methods.
Phishing emails represent one of the most common initial access vectors for malware, accounting for approximately 23% of security incidents in 2024. Anti-malware protection addresses this threat through multiple mechanisms working at different network layers. Email security scanning examines incoming messages and attachments before they reach user inboxes, identifying malicious content, suspicious links, and infected files. Advanced email security solutions integrate with anti-malware engines to detect not just known malware signatures but also suspicious attachment behaviors and phishing characteristics.
URL filtering and web protection prevent users from accidentally visiting malicious websites that host malware or credential-stealing pages. These solutions maintain real-time databases of known malicious domains and use behavioral analysis to identify newly created phishing sites. When users attempt to access flagged URLs, anti-malware solutions either block access entirely or display warnings allowing informed decision-making. This protection extends beyond traditional web browsers to include email links, instant messaging platforms, and other communication channels where malicious URLs might appear.
Credential theft prevention represents a critical anti-malware function, as stolen login credentials enable attackers to expand their access and launch secondary attacks. Anti-malware solutions monitor for keyloggers, screen capture tools, and other credential-harvesting malware that attempt to intercept user authentication information. By preventing these tools from functioning, anti-malware protects against account compromise and lateral movement within networks.
Real-time scanning represents a fundamental anti-malware capability that operates continuously in the background, monitoring files, applications, and processes as they execute. Unlike scheduled scans that run at predetermined intervals, real-time protection provides immediate threat detection and response. When users download files, install applications, or access network resources, real-time scanning examines these items before they can execute or access sensitive data. This proactive approach significantly reduces the window of opportunity for malware to establish persistence or exfiltrate data.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions extend real-time protection by collecting detailed telemetry from individual devices and analyzing this data for indicators of compromise. EDR systems maintain historical records of system activity, enabling security teams to perform threat hunting, investigate suspicious events, and identify malware that may have evaded initial detection. This forensic capability proves invaluable for understanding attack scope and implementing remediation measures.
Ransomware attacks have evolved significantly, with 92% of extortion-related incidents in 2024 involving file encryption and 60% including data exfiltration. Anti-malware solutions provide specialized protection against ransomware through multiple mechanisms. Behavioral detection identifies the characteristic file encryption patterns that distinguish ransomware from legitimate applications. When a process attempts to encrypt large numbers of files in rapid succession—a hallmark of ransomware activity—anti-malware solutions automatically block the operation and quarantine the malicious process.
File integrity monitoring tracks changes to critical system files and user data, alerting administrators to unauthorized modifications that might indicate ransomware activity. Access control enforcement restricts which processes can modify files in sensitive directories, preventing ransomware from encrypting backup files or system-critical data. These layered defenses work together to minimize ransomware impact and enable rapid recovery.
| Protection Method | Detection Capability | Response Time | Effectiveness Against | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signature-Based Detection | Known threats only | Immediate | Established malware families | Requires frequent updates; ineffective against zero-days |
| Behavioral Analysis | Known and unknown threats | Real-time | Advanced malware, zero-days | May generate false positives |
| Heuristic Analysis | Modified and new variants | Real-time | Malware variants, polymorphic threats | Requires tuning to reduce false positives |
| Sandboxing | Advanced threats | Delayed (analysis time) | Sophisticated, evasive malware | Some malware detects sandbox environment |
| Machine Learning/AI | Complex patterns | Real-time | Novel attack patterns | Requires large training datasets |
| EDR/Behavioral Monitoring | Post-execution threats | Real-time | Fileless malware, living-off-the-land attacks | Requires skilled analysts for investigation |
Organizations implementing comprehensive anti-malware solutions experience significant business benefits beyond simple threat prevention. Operational continuity improves dramatically when malware infections are prevented or rapidly contained, avoiding the costly downtime associated with system remediation. The median time to exfiltration in 2024 was approximately two days, but in nearly one in five cases, data exfiltration occurred in less than one hour, demonstrating the critical importance of rapid detection and response capabilities that anti-malware provides.
Financial protection extends across multiple dimensions. Ransomware attacks in 2024 saw median initial extortion demands increase by nearly 80% to $1.25 million, making prevention far more cost-effective than paying ransoms or managing incident response. Anti-malware prevents these attacks from succeeding in the first place. Regulatory compliance becomes significantly easier when organizations can demonstrate that they have implemented industry-standard malware protection controls. Data protection regulations including GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS all require organizations to implement appropriate technical controls to protect sensitive data, and anti-malware solutions provide documented evidence of compliance efforts.
Reputational protection represents another critical business benefit. When customers learn that their data has been compromised through a malware attack, they often take their business elsewhere. By preventing successful malware infections, organizations maintain customer trust and avoid the long-term reputational damage that follows public security breaches.
Effective anti-malware protection requires more than simply installing software; it demands a comprehensive, multi-layered approach. Endpoint protection platforms (EPPs) should be deployed across all devices including workstations, laptops, mobile devices, and servers. These solutions provide consistent protection regardless of where employees work or what devices they use. Network-level protection through firewalls and intrusion prevention systems adds another defensive layer, blocking malicious traffic before it reaches individual endpoints.
Email and web security solutions protect against the most common malware delivery vectors. Advanced email security platforms integrate multiple detection technologies to identify phishing attempts, malicious attachments, and credential-stealing attacks. Web filtering solutions prevent users from accessing known malicious websites and block drive-by download attacks.
Patch management represents a critical complementary control, as many malware attacks exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software. By maintaining current patches and security updates, organizations eliminate many attack vectors that malware relies upon. Employee security awareness training addresses the human element of security, teaching staff to recognize phishing attempts, avoid suspicious downloads, and practice safe browsing habits. Human error remains a top cause of malware infections, making user education essential to any comprehensive protection strategy.
Data backup and recovery capabilities ensure that even if malware successfully encrypts files, organizations can restore from clean backups and minimize data loss. Backups should be isolated from production systems to prevent malware from encrypting backup copies as well. Incident response planning prepares organizations to respond rapidly when malware is detected, minimizing damage and enabling faster recovery.
The cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, with threat actors developing increasingly sophisticated evasion techniques. AI-powered malware adapts faster and evades traditional detection methods by modifying its behavior based on environmental conditions. Modern anti-malware solutions counter this threat through machine learning algorithms that analyze vast datasets of threat intelligence and identify complex attack patterns that might indicate novel threats.
Fileless malware operates entirely in system memory, using legitimate system tools like PowerShell to execute malicious commands without writing files to disk. This approach evades traditional antivirus tools that rely on file scanning. Advanced anti-malware solutions detect fileless malware through behavioral analysis and memory scanning, identifying suspicious process activity and unauthorized system modifications.
Cloud and SaaS malware targets collaboration platforms and cloud-based applications where traditional endpoint protection may not apply. Modern anti-malware solutions extend protection to cloud environments through API integrations and cloud-native security agents that monitor activity within SaaS applications.
Anti-malware protection represents a fundamental requirement for modern business cybersecurity. By combining signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, heuristic examination, and machine learning capabilities, anti-malware solutions provide comprehensive defense against the diverse range of threats targeting organizations in 2025. The protection extends beyond simple virus removal to encompass ransomware prevention, phishing defense, data theft prevention, and operational continuity assurance.
Organizations that implement comprehensive anti-malware strategies—combining endpoint protection, network security, email filtering, employee training, and incident response planning—significantly reduce their exposure to cyber threats while maintaining business continuity and regulatory compliance. As threat actors continue to develop more sophisticated attack methods, anti-malware solutions must evolve in parallel, incorporating advanced detection technologies and threat intelligence to stay ahead of emerging threats. The investment in robust anti-malware protection pays dividends through prevented incidents, avoided downtime, protected customer data, and maintained organizational reputation.
PostAffiliatePro combines advanced affiliate tracking with enterprise-grade security features to protect your business operations and customer data. Our platform includes built-in protection against malicious activities, fraud detection, and secure transaction processing to ensure your affiliate network remains safe and compliant.
Discover why rootkits, bootkits, and fileless malware are the hardest viruses to remove. Learn detection methods, removal strategies, and prevention techniques ...
Learn whether adware is malware, how they differ, and why adware poses security risks. Comprehensive guide to protecting your devices from unwanted software.
Learn how adware harms your PC, including performance degradation, privacy risks, and security vulnerabilities. Discover detection methods and removal strategie...