Crawlers and Their Role in Search Engine Ranking
Crawlers accumulate data and information from the internet by visiting websites and reading the pages. Find out more about them.

Learn how web crawlers work, from seed URLs to indexing. Understand the technical process, crawler types, robots.txt rules, and how crawlers impact SEO and affiliate marketing.
Web crawlers work by sending HTTP requests to websites starting from seed URLs, following hyperlinks to discover new pages, parsing HTML content to extract information, respecting robots.txt rules, and storing collected data in searchable indexes. They systematically visit pages, extract metadata and links, and repeat the process to keep search engine databases current.
Web crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, are automated programs that systematically browse the internet to discover, download, and analyze web content. These intelligent agents form the backbone of search engine infrastructure, enabling platforms like Google, Bing, and other search services to build comprehensive indexes of billions of web pages. The primary purpose of web crawlers is to collect and organize information from websites so that search engines can quickly retrieve relevant results when users perform searches. Without web crawlers, search engines would have no way to discover new content or keep their indexes current with the latest information available online.
The importance of web crawlers extends far beyond simple search functionality. They serve as the foundation for numerous digital applications including price comparison websites, content aggregators, market research platforms, SEO analysis tools, and web archiving services. For affiliate marketers and network operators like those using PostAffiliatePro, understanding how crawlers work is essential for ensuring that affiliate content, product pages, and promotional materials are properly discovered and indexed by search engines. This visibility directly impacts organic traffic, lead generation, and ultimately, affiliate commission opportunities.
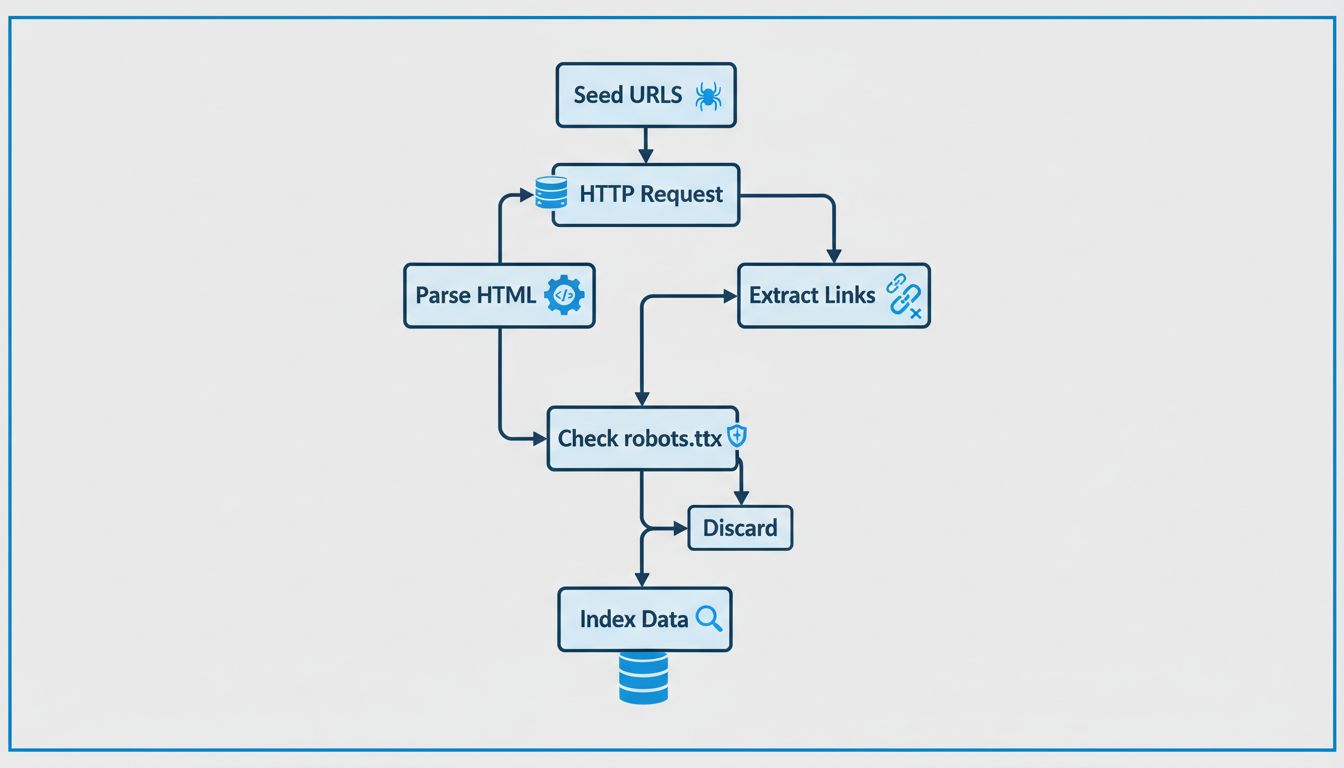
Web crawlers follow a methodical and structured process to systematically explore the internet. The process begins with seed URLs, which are known starting points such as homepage URLs, XML sitemaps, or previously crawled pages. These seed URLs serve as the entry point for the crawler’s journey through the web. The crawler maintains a queue of URLs to visit, often called the “crawl frontier,” which continuously grows as new links are discovered during the crawling process.
When a crawler reaches a URL, it sends an HTTP request to the web server hosting that page. The server responds by sending back the HTML content of the page, similar to how a web browser loads a page when you visit it. The crawler then analyzes this HTML code to extract valuable information including page text content, meta tags (such as title and description), images, videos, and most importantly, hyperlinks to other pages. This link extraction is crucial because it allows the crawler to discover new URLs that haven’t been visited yet, which are then added to the crawl queue for future visits.
| Crawler Process Stage | Description | Key Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Initialization | Starting the crawl process | Load seed URLs, initialize crawl queue |
| Request & Retrieval | Fetching page content | Send HTTP requests, receive HTML responses |
| HTML Analysis | Parsing page structure | Extract text, metadata, links, media |
| Link Extraction | Finding new URLs | Identify hyperlinks, add to crawl queue |
| robots.txt Check | Respecting site rules | Verify crawling permissions before visiting |
| Content Storage | Saving information | Index data in searchable database |
| Prioritization | Determining next pages | Rank URLs by importance and relevance |
| Repetition | Continuing the cycle | Process next URL in queue |
Before visiting a new URL on a domain, responsible crawlers check the robots.txt file located in the root directory of that domain. This file contains instructions that website owners use to communicate with crawlers about which pages can be crawled and which should be avoided. For example, a website owner might use robots.txt to prevent crawlers from accessing sensitive pages, duplicate content, or resource-heavy sections that could overload their servers. Most legitimate search engine crawlers respect these instructions to maintain good relationships with website owners and avoid causing performance problems.
Modern web crawlers have evolved significantly to handle the complexity of contemporary websites. Many websites today use JavaScript to dynamically generate content after the page loads, meaning the initial HTML response doesn’t contain all the page content. Advanced crawlers now use headless browsers to render JavaScript and capture dynamically loaded content that wouldn’t be visible to traditional crawlers. This capability is essential for crawling single-page applications, interactive dashboards, and modern web applications that rely heavily on client-side rendering.
Crawlers implement sophisticated prioritization algorithms to make efficient use of their crawl budget—the limited number of pages they can crawl within a given timeframe. These algorithms consider multiple factors including page authority (determined by backlink quality and quantity), internal link structure, content freshness, traffic volume, and domain reputation. High-authority pages and frequently updated content receive more frequent crawl visits, while less important or static pages may be visited less often or skipped entirely. This intelligent prioritization ensures that crawlers focus their resources on the most valuable and frequently changing content.
Crawl delay and rate limiting are important mechanisms that prevent crawlers from overwhelming web servers. Responsible crawlers implement pauses between requests and respect the crawl-delay directives specified in robots.txt files. This polite crawling behavior protects website performance and user experience by ensuring that crawler traffic doesn’t consume excessive server resources. Websites that load slowly or return errors may experience reduced crawl frequency as crawlers automatically slow down to avoid causing problems.
Different types of web crawlers serve distinct purposes in the digital ecosystem. General web crawlers are deployed by major search engines to crawl the entire internet indiscriminately, creating comprehensive indexes that power search results. These crawlers are designed for maximum coverage and operate continuously to discover new content and update existing indexes. Vertical or specialized crawlers focus on specific industries or content types, such as job crawlers that search job boards, price comparison crawlers that collect pricing data from e-commerce sites, or research crawlers that index academic papers and scientific publications.
Incremental crawlers specialize in efficiency by focusing only on new or recently modified content rather than re-crawling entire websites repeatedly. This approach significantly reduces server load and bandwidth consumption while keeping indexes relatively current. Focused crawlers use sophisticated algorithms to search for content on specific topics or keywords, intelligently prioritizing pages likely to contain relevant information. Real-time crawlers continuously monitor websites and update their collected data in real-time or near real-time, making them ideal for news aggregation and social media monitoring applications.
Parallel crawlers and distributed crawlers represent the infrastructure-heavy end of the crawler spectrum. Parallel crawlers run on multiple machines or threads simultaneously to dramatically increase crawling speed and throughput. Distributed crawlers spread the workload across multiple servers or data centers, allowing them to process massive amounts of data efficiently. Large search engines like Google use distributed crawler architectures to handle the billions of pages on the internet.
Web crawlers play a fundamental role in search engine optimization because they determine which pages get indexed and how search engines understand your content. If crawlers cannot access your pages, those pages will not appear in search results regardless of their quality or relevance. Common crawling issues that prevent proper indexing include pages blocked by robots.txt directives, broken internal links that lead to 404 errors, slow page load times that cause crawlers to timeout, and JavaScript rendering problems that prevent crawlers from seeing dynamically generated content.
Website owners can optimize crawler access through several key strategies. Clear site architecture with logical navigation hierarchies helps crawlers understand page relationships and importance. Internal linking signals to crawlers which pages are most important and helps distribute crawl budget efficiently across your site. XML sitemaps explicitly list all important pages, ensuring crawlers don’t miss any content even on large or complex websites. Fast page load times encourage crawlers to visit more pages within their allocated crawl budget, while fresh, regularly updated content signals that a site deserves more frequent crawl visits.
For affiliate marketers using platforms like PostAffiliatePro, ensuring proper crawler access is critical for driving organic traffic to affiliate content. When your affiliate product pages, comparison articles, and promotional content are properly crawled and indexed, they have the opportunity to rank in search results and attract qualified traffic. Poor crawlability can result in missed indexing opportunities and reduced visibility for your affiliate offers.
Website owners have several mechanisms to control how crawlers interact with their sites. The robots.txt file is the primary tool, containing directives that specify which user-agents (crawler types) can access which parts of the website. A well-configured robots.txt file can prevent crawlers from wasting resources on duplicate content, staging environments, or resource-intensive pages while allowing them to freely crawl important content. The robots meta tag appears in individual page HTML and provides page-level control, allowing specific pages to be excluded from indexing or their links to be ignored.
The nofollow link attribute tells crawlers not to follow specific hyperlinks, useful for preventing crawlers from following links to untrusted external sites or user-generated content. These control mechanisms work together to give website owners fine-grained control over crawler behavior while maintaining good relationships with search engines. However, it’s important to note that malicious web scrapers and aggressive bots often ignore these directives entirely, which is why additional security measures like rate limiting and bot detection are sometimes necessary.
For affiliate network operators and marketers, understanding web crawler behavior directly impacts business success. Crawlers determine the visibility of affiliate product pages, comparison content, and promotional materials in search results. When PostAffiliatePro users optimize their affiliate websites for proper crawling, they increase the likelihood that their content will be discovered by search engines and ranked for relevant keywords. This organic visibility drives qualified traffic to affiliate offers, increasing conversion opportunities and commission earnings.
Affiliate networks benefit from crawler activity in multiple ways. Search engine crawlers help distribute affiliate content across the internet, increasing brand awareness and reach. Crawlers also enable price comparison sites and content aggregators to discover and feature affiliate products, creating additional traffic sources. However, affiliate marketers must also be aware of malicious crawlers and scrapers that might copy affiliate content or engage in click fraud. Implementing proper rate limiting, bot detection, and content protection measures helps protect affiliate network integrity while allowing legitimate crawlers to function properly.
PostAffiliatePro provides comprehensive tracking and reporting capabilities that complement proper crawler optimization. By ensuring your affiliate content is properly crawled and indexed, combined with PostAffiliatePro’s advanced tracking and analytics, you can maximize the visibility and profitability of your affiliate network. The platform’s real-time commission tracking and intelligent reporting help you understand which affiliate channels drive the most valuable traffic, allowing you to optimize your network strategy accordingly.
Just like web crawlers systematically discover and index content, PostAffiliatePro systematically tracks and optimizes your affiliate relationships. Our platform provides real-time tracking, comprehensive reporting, and intelligent commission management to help you build a thriving affiliate network.
Crawlers accumulate data and information from the internet by visiting websites and reading the pages. Find out more about them.
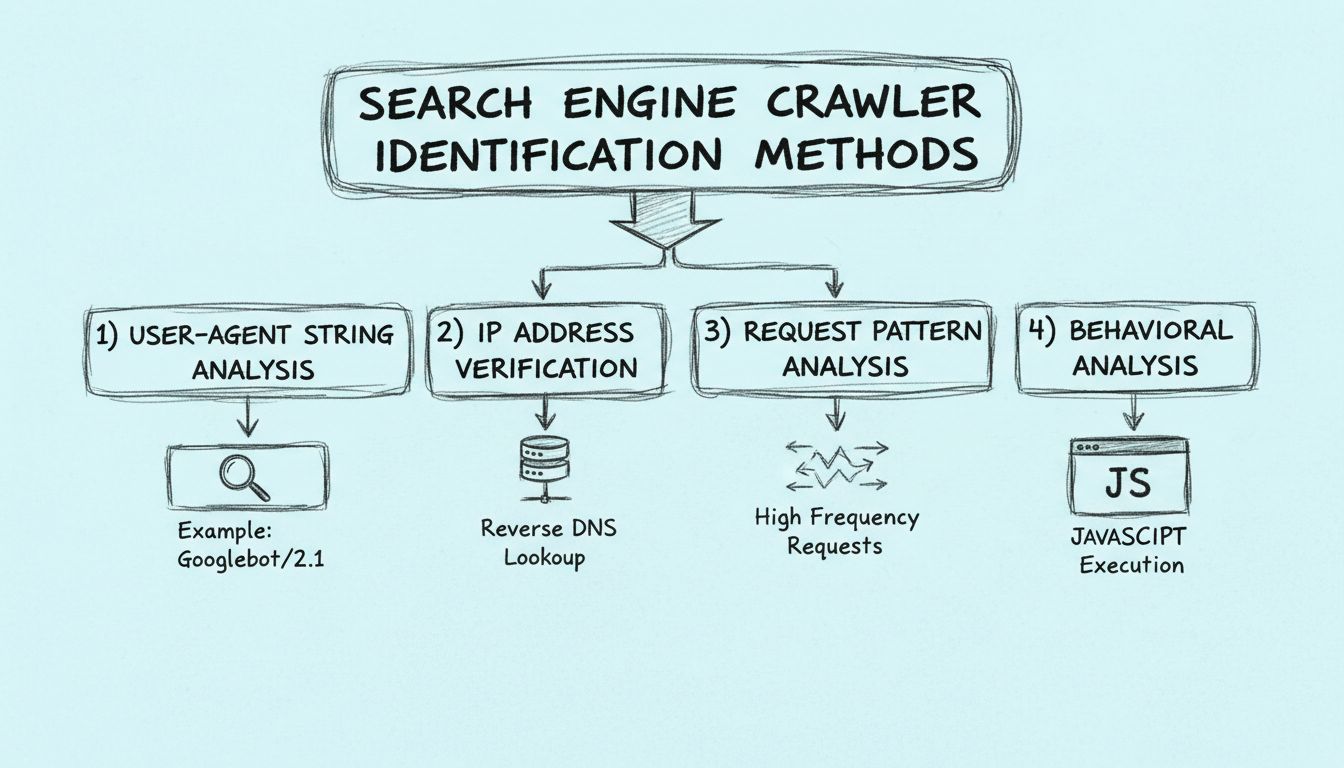
Learn how to identify search engine crawlers using user-agent strings, IP addresses, request patterns, and behavioral analysis. Essential guide for webmasters a...
Spiders are bots created for spamming, which may cause your business a lot of problems. Learn more about them in the article.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.